Writing a layout provider¶
Concept¶
We've tried to devise our architecture in a generic way that's easy to extend and work with.
The illustration below is a top level overview of how artifact management is implemented in Strongbox within Storages, Repositories and Layout Providers:
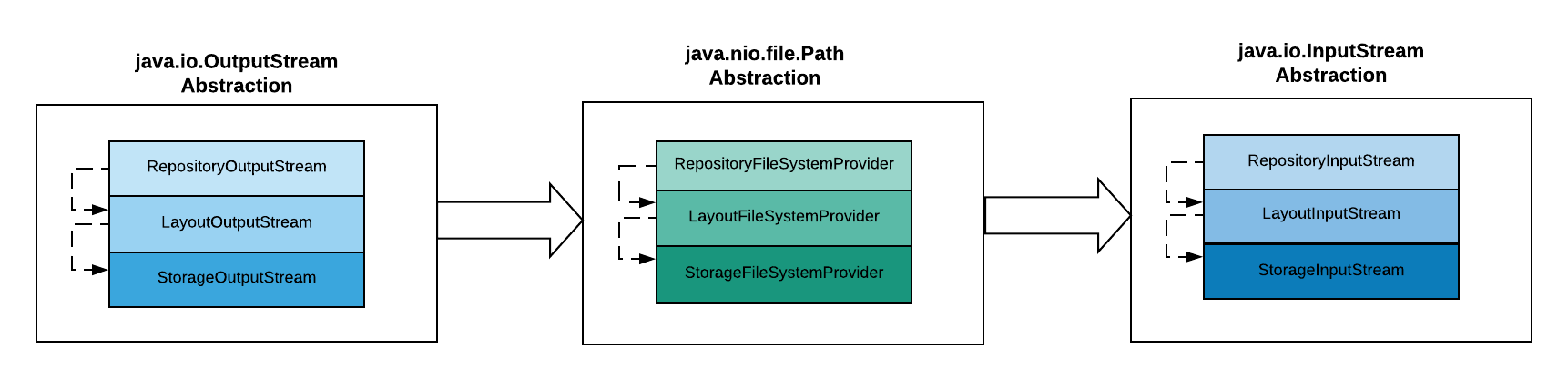
There are three layers and each of them decorates the underlying layer with the logic it's responsible for. For example, the following layer implementations are possible:
Repository
- Hosted
- Proxy
- Group
Layout
- Maven
- NPM
- NuGet
- Raw
Storage
- File system
- AWS S3 (not yet implemented)
- Google Cloud (not yet implemented)
All of the layers are loosely coupled, so implementations don't depend on each other. With the Decorator Pattern
concept you can have any layer implementation combinations you need: Hosted+Maven+ File System, Group+ Npm+ AWS etc.
Layout Implementation¶
We can say that artifacts are just regular files, so our implementation is mainly based on the common JDK File I/O (Featuring NIO.2) entities.
This is how it looks like:
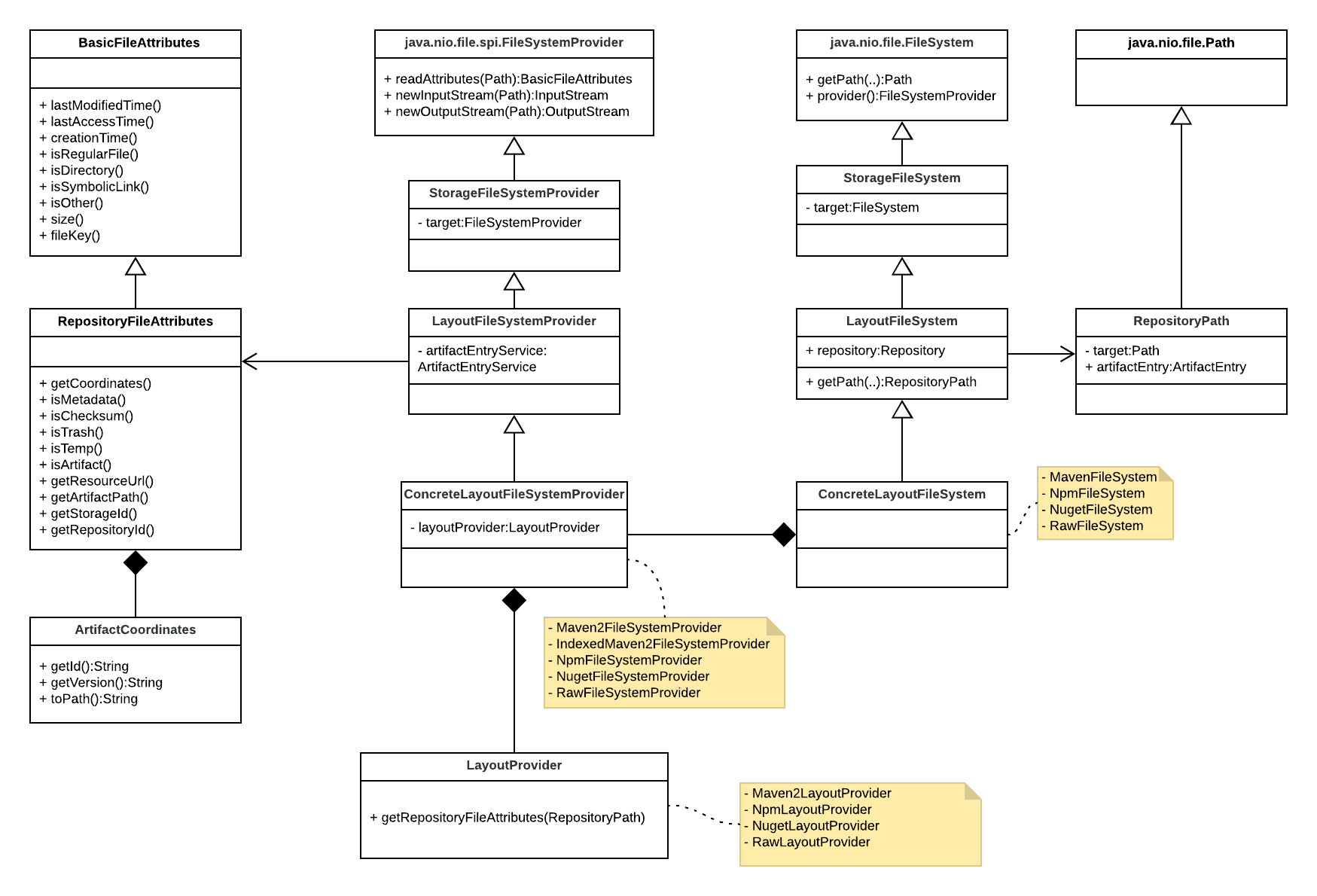
You will need to implement following entities:
ConcreteLayoutFileSystemProviderConcreteLayoutFileSystemLayoutProviderArtifactCoordinates
Artifact Coordinates¶
Each layout implementation should be able to identify artifacts and the Artifact Coordinates serves this purpose.
These are the minimal requirements for ArtifactCoordinates.java implementations:
- Each ArtifactCoordinates implementation should have an id and version.
- Each id and version pair must be unique per repository.
- There should be a transitive function to get ArtifactCoordinates from Path and vice-versa.
Notes
- Each layout implementation should be placed in separate module under the
strongbox-storage/strongbox-storage-layout-providersmodule. - There should be thorough unit tests that check the implementation
- There should be a layout-specific Artifact Generator implemented which will be used for test purpose
Artifact Controller¶
Once you have created your module and created an implementation of the ArtifactCoorsinates, you can start implementing
the protocol specific API. Most of the build and artifact management tools are using HTTP to interact with their
end-points and in Strongbox we use Spring MVC for this. The BaseArtifactController.java should be extended with
protocol-specific API methods (download, upload etc.).
Notes
There should be REST Assured based unit tests to check that artifact downloads/uploads handled with HTTP 200 response code
Layout specific I/O extension¶
To make the layout implementation truly usable, there should be some layout specific I/O, such as Streams
(InputStream, OutputStream) and File System related entities (FileSystemProvider, FileSystem, LayoutProvider).
Below is the set of base classes which need to be extended:
LayoutFileSystemLayoutFileSystemProviderAbstractLayoutProvider
Almost all components in Strongbox are managed by Spring's IoC container, the same goes for the for layout-related components and there should be the following factories to put everything into context:
LayoutFileSystemProviderFactoryLayoutFileSystemFactory
Putting It All Together¶
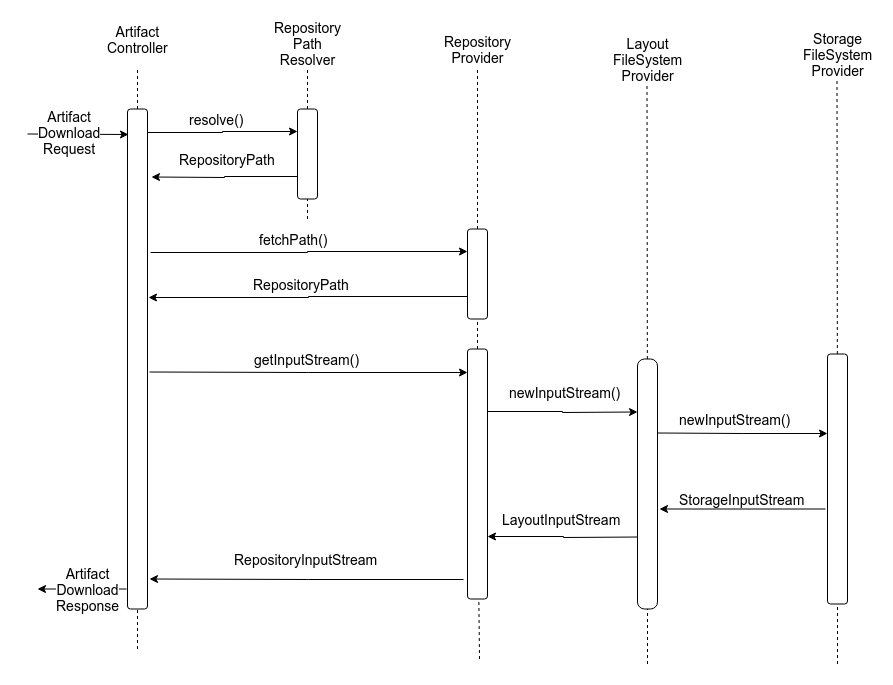
Strongbox has plugable layout providers, so once you have impelemted all the extension points, it should work out of the box.
Below you can see how the general flow goes, based on the artifact download example:
See Also¶
- Artifact Coordinates
- Artifact Coordinate Validators
- Storages
- Repositories
- Layout Providers
- Maven 2 Layout Provider
- NPM Layout Provider
- NuGet Layout Provider
- Raw Layout Provider